
There are various methods for detecting plant extracts, and the following are commonly used detection methods by INNA company:
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)

Principle: Using liquid as the mobile phase, a high-pressure infusion system is employed to pump single solvents with different polarities or mixed solvents with different ratios, buffer solutions, and other mobile phases into a chromatographic column containing a stationary phase. After the components in the column are separated, they enter the detector for detection, thereby achieving analysis of the sample.
Features: High resolution, high sensitivity, good reproducibility, capable of qualitative and quantitative analysis of various components in plant extracts.
Application: Widely used for chemical composition analysis of plant extracts, providing strong support for product quality control.
UV Vis spectrophotometer

Principle: A method of analysis and measurement that utilizes the absorption of radiation in the spectral range of 10~800nm by molecules of certain substances.
Features: Simple, fast, high sensitivity, good accuracy, excellent selectivity, easy operation, fast analysis speed.
Application: Widely used for qualitative and quantitative determination of organic and inorganic substances, suitable for the detection of certain specific components in plant extracts.
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis
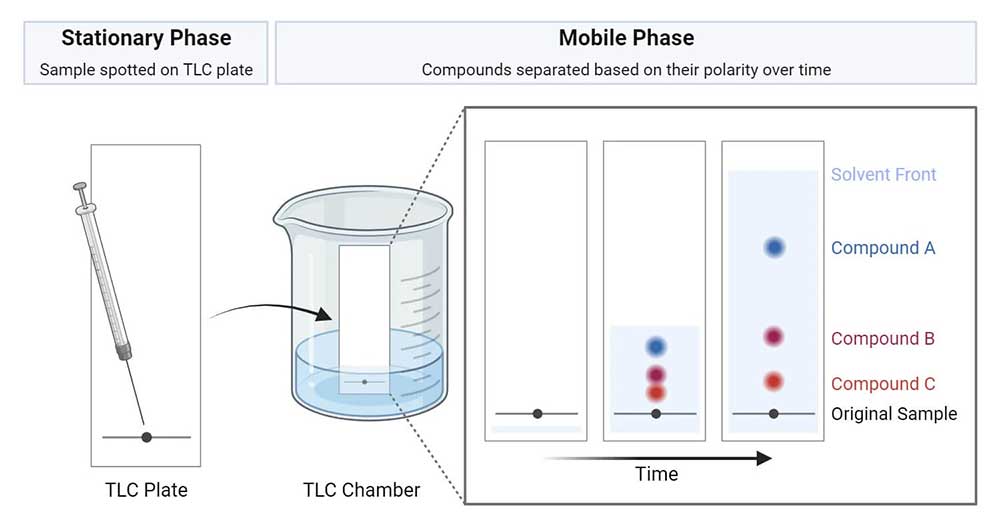
Principle: Apply a suitable stationary phase onto a glass plate, plastic or aluminum substrate to form a uniform thin layer. After sampling and unfolding, the method is used to compare the specific shift value (Rf) of the chromatogram obtained by the same method with the appropriate reference substance, for drug identification, impurity detection, or content determination.
Characteristic: It is an important experimental technique for rapid separation and qualitative analysis of small amounts of substances.
Application: Used for the detection of proportional extracts.
Gas chromatography (GC)

Principle: Chromatography using gas as the mobile phase.
Features: Suitable for detecting volatile components.
Application: Suitable for detecting volatile components such as essential oils and aroma components in plant extracts, providing important basis for aroma analysis and quality control of products.
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
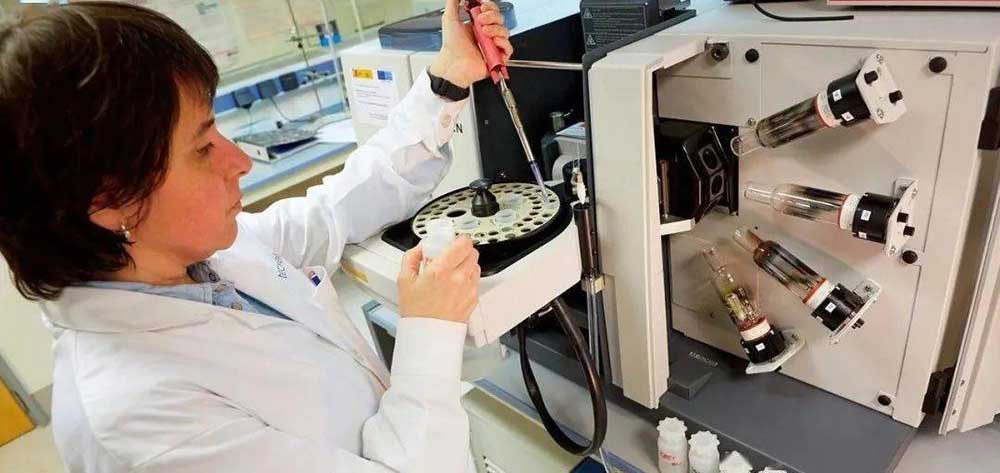

Principle: A quantitative analysis method based on the absorption intensity of corresponding atomic resonance radiation lines in the ultraviolet and visible light ranges by the outer electrons of the ground state atoms in the gaseous state.
Characteristics: Mainly suitable for the analysis of trace and trace components in samples.
Application: Used for detecting heavy metal content in extracts.
Mass spectrometry (MS)
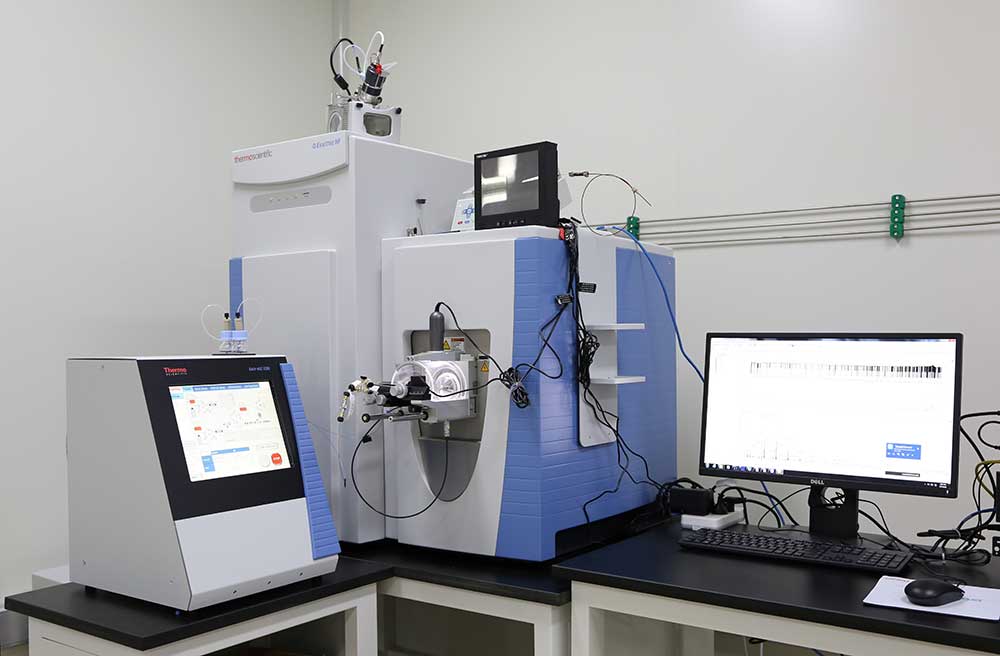

Principle: A highly sensitive detection method that performs component analysis by measuring the mass charge ratio (m/z) of sample molecules.
Characteristics: It can provide rich structural information and is often used in combination with HPLC, GC and other technologies for the identification and quantitative analysis of unknown components in plant extracts.
Application: Helps to gain a deeper understanding of the chemical composition of plant extracts.
Infrared spectroscopy (IR)
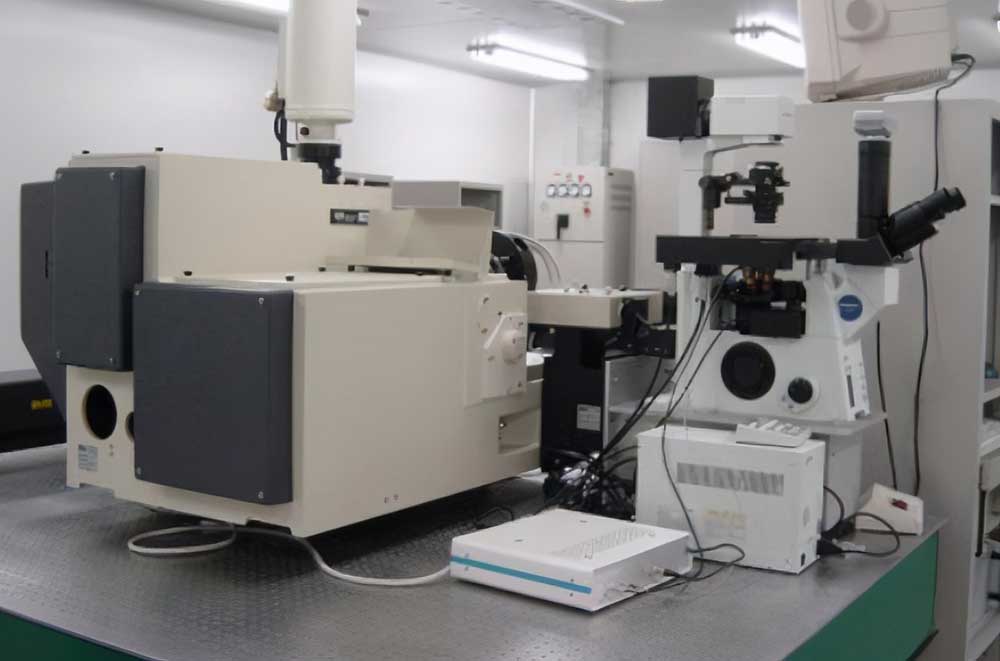

Principle: By measuring the absorption spectrum of the sample in the infrared region, information about the molecular structure can be obtained.
Features: Can be used for identification and structural analysis of functional groups in plant extracts.
Application: Provide support for product quality control and research and development.
In practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate detection methods based on the characteristics and detection requirements of plant extracts. Meanwhile, with the continuous advancement of science and technology, new detection methods and techniques are constantly emerging, providing more comprehensive and accurate means for the quality testing of plant extracts.

